Parotidectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the parotid gland, which is the largest salivary gland located in front of the ear. The parotid gland produces saliva, which helps in the digestion of food. For patients requiring advanced care, Salivary & Parotid Gland Surgery in Kukatpally offers specialized treatment options to restore oral health and function.
How it is performed
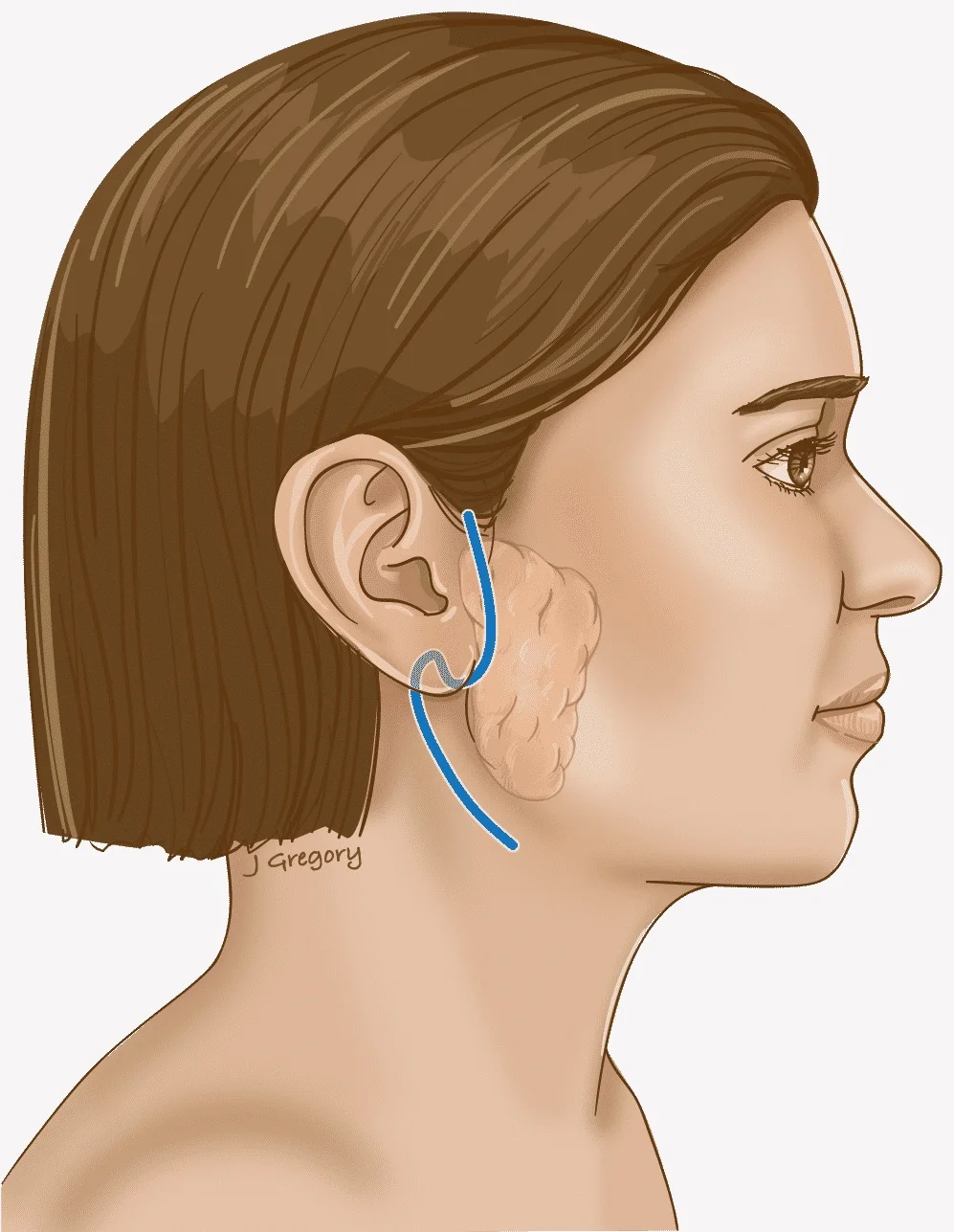
Parotidectomy is a surgical procedure that is typically performed under general anesthesia. The procedure involves making an incision in front of the ear and along the jawline to expose the parotid gland.
Once the gland is exposed, the surgeon carefully separates it from the surrounding tissues, including the facial nerve that runs through the gland. This is done to avoid damage to the nerve and to preserve its function. If the surgery is being performed to remove a tumor, the surgeon will also remove the tumor along with the gland. After the gland has been removed, the surgeon will use sutures to close the incision. A small drainage tube may be inserted to remove any excess fluids from the surgical site.
The length of the procedure depends on the specific case and the extent of the surgery. It may take anywhere from a few hours to several hours. After the procedure, patients are typically monitored in a recovery room for a few hours before being discharged. They may need to stay in the hospital for a day or two if complications arise.
Why is the surgery done
Parotidectomy surgery is done for a variety of reasons, including:
- Tumor removal from the parotid gland
- Salivary gland stone removal: Sometimes, stones may form in the ducts of the parotid gland, leading to pain, swelling, and infection.
- Infection: In rare cases, the parotid gland may become infected, leading to inflammation and pain which will need to be treated through surgery
- Chronic inflammation: Some patients may develop chronic inflammation of the parotid gland, which can lead to recurrent swelling, pain, and other symptoms. In such cases, surgical removal of the gland may be necessary to relieve symptoms.
- Biopsy: In some cases, a small tissue sample (biopsy) may be required to diagnose a suspected parotid gland condition. Parotidectomy surgery may be performed to obtain this sample for testing.
What to expect post surgery
After a parotidectomy surgery, it is normal to experience some discomfort, swelling, and bruising in the face and neck. Pain medication and ice packs can help manage these symptoms. Here are some things you can expect after the surgery:
- Hospital stay: Most patients can go home the same day or the day after the surgery. However, in some cases, an overnight hospital stay may be required.
- Swelling and bruising: Swelling and bruising are common after parotidectomy surgery and can last for several weeks. Ice packs can help reduce swelling, and over-the-counter pain medication can help manage discomfort.
- Numbness: Numbness in the face and neck is common after parotidectomy surgery and may last for several weeks to several months. This is usually temporary and should resolve over time.
- Drainage tube: In some cases, a small drainage tube may be inserted at the surgical site to remove excess fluids. The tube is usually removed within a few days after the surgery.
- Follow-up appointments: You will need to see your doctor for follow-up appointments to monitor your healing and ensure that there are no complications.
- Facial exercises: Your doctor may recommend facial exercises to help improve facial muscle strength and prevent long-term weakness or drooping.
- Diet and activity restrictions: Your doctor may recommend specific dietary and activity restrictions, such as avoiding strenuous activity and eating soft foods for a few days after the surgery.
Risks associated with the surgery
Like all surgical procedures, parotidectomy surgery carries some risks. Here are some potential risks and complications associated with parotidectomy surgery:
- Facial nerve damage
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Salivary fistula
- Facial numbness
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What are salivary gland tumors, and are they treatable?
Salivary gland tumors are growths in salivary glands, treatable with surgery and expert care.
-
Where can I get expert treatment for salivary gland tumors?
Amrita ENT Hospital offers specialized diagnosis, advanced surgery, and comprehensive tumor care.
-
What causes salivary gland tumors to develop?
Causes include radiation exposure, genetic factors, and lifestyle habits like smoking.
-
Are all salivary gland tumors cancerous?
No, many tumors are benign, but early diagnosis ensures proper treatment.
-
What symptoms indicate a salivary gland tumor?
Symptoms include swelling, pain, difficulty swallowing, and facial nerve weakness.
-
Will salivary gland tumor surgery leave a visible scar?
Our expert surgeons minimize scarring with precise, cosmetically conscious techniques.
-
How long does recovery take after tumor surgery?
Most patients recover within weeks with proper post-surgery care.
-
Can salivary gland tumors affect facial movement?
Some tumors may impact facial nerves; our surgeons prioritize nerve preservation.
-
Why choose Amrita ENT for salivary gland tumor treatment?
We offer expert surgeons, advanced technology, and personalized patient care.
-
Are pediatric salivary gland tumors treated at Amrita ENT?
Yes, our specialists treat children with advanced, gentle care.
-
What follow-up care is required after tumor treatment?
Regular check-ups ensure recovery and monitor for any recurrence.
